What is Textile Fiber Sampling?
Textile fiber sampling is the process of collecting a sample from a large number of textile fiber material. This allows researchers or analysts to select a representative portion, making it possible to draw conclusions about the entire batch or population without needing to examine every individual piece.
The manufactures of textile is largely a system of mass production. To test every item would be impossible, we therefore test samples.

Population:
The whole bulk of the material available for testing is termed as population.
Sample:
A sample is a smaller portion basically chosen to represent a larger population. In other terms, it serves as a selected unit or part, acting as a representative of a lot, consignment, or design. By using the sample, we can effectively demonstrate both the qualities and defects of the entire consignment. A sample must consists of a number of individuals (An individual is one number of the population).
Purposes of Textile Fiber Sampling:
- To represent a portion that reflects the characteristics of the entire population.
- To save time.
- To lower costs.
- To ensure high quality.
- To understand the true characteristics of the population.
- To avoid the damaging effects of certain tests.
- To draw reliable conclusions or make informed decisions based on the sample data.
Factors Influencing Textile Fiber Sampling Method:
Factors that determine textile fiber sampling methods involve considerations such as-
- Population size.
- Required precision.
- The shape of the materials.
- The quantity of available resources.
- The nature of the test.
- The type of testing instrument.
- The information needed.
- Time limitations.
- The chosen sampling technique
These elements all play a role in shaping the sampling process’s effectiveness and reliability.
Different Types of Textile fiber Sampling Method:
There are normally two main types of sampling methods-
- Random Sampling.
- Biased Sampling.
1. Random Sampling Method:
- In the random textile fiber sampling method, every individual in the population has an equal chance of being selected.
- The sample size must be large enough to capture all variations within the population.
2. Biased Sampling Method:
- In the biased textile fiber sampling method, the selection of individuals is influenced by factors other than chance.
- Bias can arise from the physical characteristics of the individual or their position relative to the person conducting the sampling.
- For example, longer fibers are more likely to be selected from a strand of material than shorter fibers.
Differences Between Random Sampling & Biased Sampling Method:
In textile fiber sampling methods, there are some differences between random and biased sampling methods. The differences are as follows:
| Random sampling | Biased sampling |
| Each portion of the population has an equal probability of being a part of it. | Each portion of the population has not an equal probability of being a part of it. |
| It is not affected by factors such as physical characteristics. | It is affected by factors such as physical characteristics. |
| Random sampling does not depend on the position of the sampling person. | Biased sampling depends on the position of the sampling person. |
| Sample represents the bulk truly. | Sample does not represent the bulk truly. |
| Test result is not dependable. | Dependable test result. |
| The random approach is seen to be the most effective. | The random approach may be negligible. |

Sampling Method for Different Textile Materials:
- Sampling for determination of fiber properties.
- Sampling for determination of yarn properties.
- Sampling for determination of fabric properties.
Sampling For Determination of Fiber Properties:
It depends upon the form in which the fiber is available. Different techniques for different form of fibers-
- Fiber in bale form.
- Fiber in sliver form.
- Fiber in yarn form.
Methods For Textile Fiber Sampling:
- Length and extent biased sample
- The squaring technique.
- The cut squaring method.
- The zoning technique (for raw cotton).
- The tong sampling method (for wool).
- The core sampling method (for wool).
- Dye sampling method (for wool).
The Zoning Technique For Raw Cotton:
The zoning technique for raw cotton involves dividing the cotton into different sections or zones based on specific criteria, such as fiber length or quality. This method helps in organizing and managing cotton for more efficient processing and ensures better consistency in the final product.
If the material is not homogeneous, multiple sub-samples must be randomly taken from various locations within the bulk. The number of sub-samples required depends on the level of heterogeneity in the bulk, which can be determined through experimentation. The following procedure outlines how to prepare a sample for the stapling test using a comb sorter.
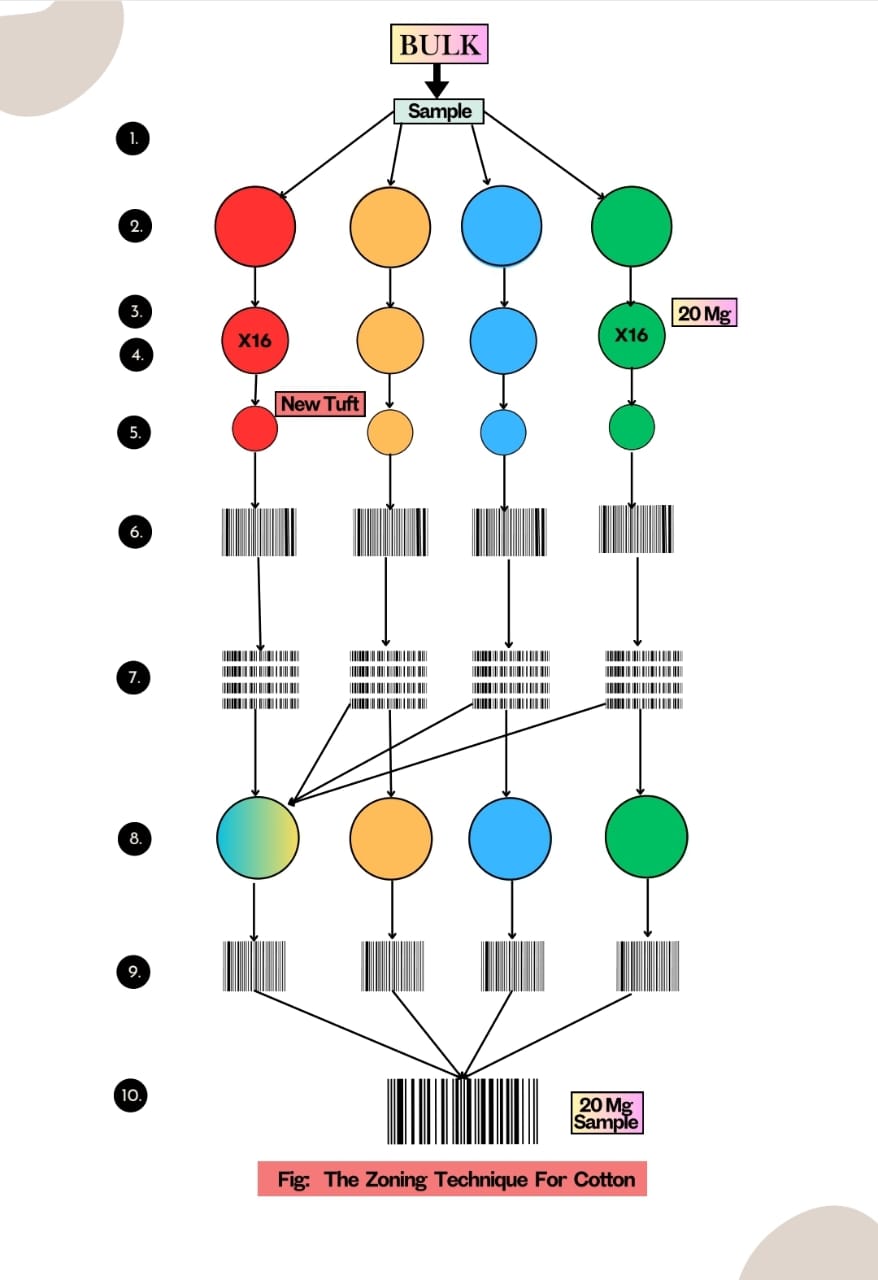
Steps In Zoning Technique:
Step 1: From the bulk, a sample of about 2 oz is prepared by selecting about
eighty large tufts chosen, so far as is possible, over the bulk.
Step 2: Divide this sample into four quarters.
Step 3: Take sixteen small tufts at random from each quarter, size approximately 20 mg.
Step 4: Each tuft shall be halved four times, discarded alternately with right and left hands and turning the tuft through a right angle between successive halving. Sixteen ‘wisps’ are thus produced from each quarter sample.
Step 5: Combine each set of wisps into a tuft.
Step 6: Mix each tuft in tuft by doubling and drawing between the fingers.
Step 7: Divide each tuft into parts.
Step 8: Obtain four new tufts by combining a part of each of the former tufts.
Step 9: Mix each new tuft again by doubling and drawing.
Step 10: Take a quarter from each tuft to make the final sample.
References:
- Principles of Textile Testing by J E Booth.
- Handbook of Textile Testing and Quality Control by E. B. Grover, Elliot Brown Grover, Dame Scott Hamby.
- Physical Testing of Textiles by B.P. Saville.
To learn more on textile testing and laboratory accreditation you can check on the following article:
- Testing Of Textiles: Why Is It Important For The Textile And Apparel Industries?
- Fabric Abrasion Resistance: Martindale Abrasion Testing Process
- Fabric Hand feel evaluation by Fabric Touch Tester (FTT)
- Color Fastness test
- Washing fastness test method: ISO 105 C06
- ISO/IEC 17025 Laboratory Accreditation Process
- ISO/IEC 17025 Laboratory Accreditation Advantages
- KEY STEPS FOR CONDUCTING AN EFFECTIVE QMS INTERNAL AUDIT




2 thoughts on “10 comprehensive steps in textile fiber sampling method”
Best wishes sir🌹
Thanks for the support.