CVC knit fabric dyeing:
CVC stands for Chief Value of Cotton. This fabric blend typically contains a higher percentage of cotton than polyester. For example, 80/20 CVC, 60/40 CVC, and so on. Here, 60% cotton and 40% polyester yarn are used, or 60/40 CVC. In order to achieve a consistent and long-lasting color, CVC knit fabric dyeing is a sophisticated procedure that calls for careful consideration of the fiber content of the fabric, optimal dye selection, regulated dying conditions, and extensive fixation and after-treatment steps.
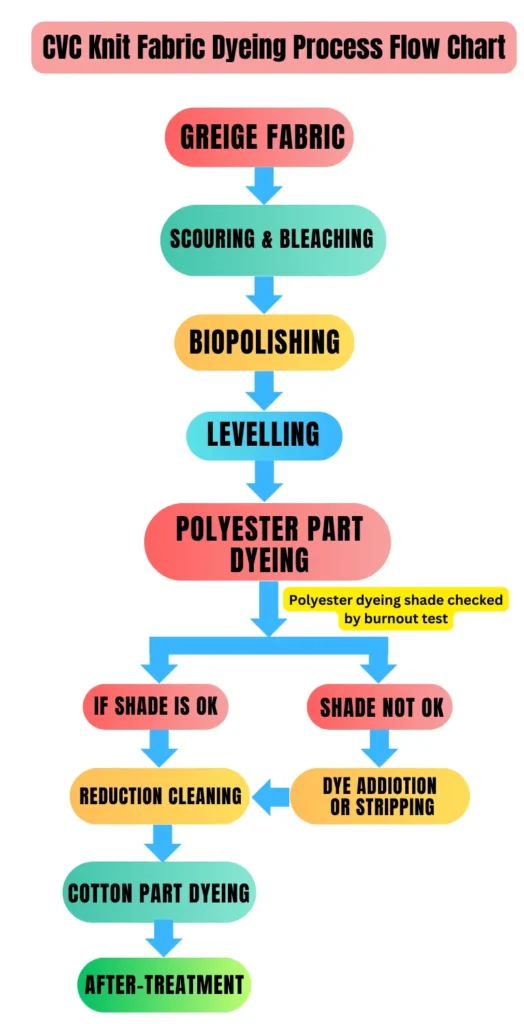
CVC Knit Fabric Dyeing Process flow diagram:
CVC Knit Fabric Dyeing Description:
1) Scouring & Bleaching of CVC Greige fabric:
Firstly, the fabric is scoured with NaOH to remove oil, wax, dust and other natural impurities from the CVC Greige fabric. And then bleaching is done with H2O2 to remove the natural color from the CVC Greige fabric. In this step, other chemicals are used such as Wetting agent, Sequestering agent etc.

2) Biopolishing:
This process is also known as Enzymatic singeing. The reason for saying Enzymatic singeing is that in Singeing, the hairiness on the surface of the woven fabric are removed with the help of flame. On the other hand in Biopolishing, the hairiness of the knitted cotton fabric is removed with the help of enzymes.
Biopolishing is a chemical process where the extra hairs in the knitted cotton fabric are weakened with the help of cellulase enzyme and removed with the help of water pressure.
The changes that occur in the fabric by biopolishing are:
1) Reduces fabric pilling.
2) Gives the fabric a smooth and soft hand feel.
Biopolishing is usually done at 45°-55°C and at acidic pH . A hot wash is then given at 80°C to deactivate the enzyme.
3) Levelling:
A levelling agent is used before the dyeing step begins in the fabric. The purpose of using the leveling agent is to spread the dye chemicals evenly on the fabric.
Also, in this step before fabric dyeing, Sequestering agent, Anti-creasing agent, Defoaming agent etc. are used.
4) Polyester Part Dyeing:
In the first stage of dyeing, the polyester part is first dyed with the help of disperse dye. Then the cotton part is dyed. So this dyeing process is called Double part dyeing.
Now the question is why the polyester part is dyed first?
The reason is that Polyester fabric is dyed at a temperature of 130°C whereas Cotton fabric is dyed at a temperature of 60/80°. If the Cotton part is dyed before the Polyester part dyeing, Cotton part’s dye will be removed because of the high temperature (130°C) of the Polyester dyeing. .
And the effect that comes when dyeing any one part of CVC fabric is called Marl effect.

Polyester Dyeing Shade Check by Burnout Test:
Since this process is done in 2 steps i.e. one part (Polyester) is dyed first, than cotton part dyed. So, it is difficult to understand whether the dyeing of the polyester part has been done properly according to the shade for the white part of the cotton. That is why there is a burnout test.
The most interesting thing is that through this test the cotton part in CVC knit fabric is completely burnt with 70% H2SO4 and 30% water. Due to which it is easy to understand whether the dyeing shade requirement is done in the remaining polyester part.
If the dyeing shade of the polyester part matches, then it goes to the next process (Reduction Cleaning). If the shade does not match, then dye addition/topping or stripping is done.

5) Reduction Cleaning:
Reduction cleaning is usually done after polyester fabric dyeing. Where the excess dyes on polyester or cotton are removed. So that there is no problem in entering the dye to the cotton part in the next step. Reduction cleaning is done with the help of reducing agent.
For medium to dark shade fabric usually requires the following parameters:
Reducing agent: 2gm/litre
Time: 30min
Temperature: 80°C
PH: 8.5-9.5
In case of dark to extra dark shade, reduction cleaning may have to be done 2 times. Then the time may take 1-2 hours more.
NaOH and Na2S2O4 (Hydrose) are widely used as reducing agents.
6) Cotton Part Dyeing:
After polyester part dyeing and reduction cleaning, cotton part dyeing is done with reactive dye at 60°/80°C temperature. Then the shade is checked, if it is OK, it goes to the next step and if the shade is not OK, dye addition/topping is done.

7) After-treatment:
The last step of dyeing is After-treatment. In this step, the fabric is soaped with the help of detergent, as a result of which the unfixed dyes are removed from the fabric surface. And in this step, the fabric is made soft and smooth with the help of softener.

Nowadays CVC knit fabric is in high demand because, the cost of CVC fabric is lower than 100% cotton and CVC fabric is used instead of cotton to increase the durability of the fabric. 100% cotton is relatively comfortable but the fabric wears more with less use.

Normally CVC is used a lot for fleece fabric because the back side of the fleece fabric is brushed. And if you brush with 100% cotton, the brush is less likely to be uniform. On the other hand, due to the presence of polyester in the binding in CVC, the brush will have uniform brushing.
The whole process takes about 16 hours to complete. If such fabric is not dyed in double part separately then marl effect occurs in the fabric.
References:
- Cellulosics Dyeing Edited By John Shore
- Basic Principles Of Textile Coloration – Arthur D. Broadbent
- Textile Preparation and Dyeing by A K Roy Choudhury
- Dyeing and Chemical Technology of Textile Fibers by E.R. Trotman
- Chemistry of dyes and principles of dyeing by Shenai V.A.
To learn more on different dyes chemical and dyeing applications you can check on the following article:
- Reactive Dyeing In Textile: Mechanism, Classification And Steps
- Reactive Dyeing: Process And Method
- Disperse Dyes: Properties, Mechanisms, And Application Methods In Textile Industry
- 100% Cotton Knit Fabric Dyeing Process – Exhaust Dyeing Method
- Chemicals Used In Textile And Dyeing Industries
- Cold Pad Batch (CPB) dyeing process



