Yarn Count:
Count is a numerical expression of a yarn, which defines fineness & coarseness. A definition of yarn count is given by the textile institute-” Count, a number indicating the mass per unit length or length per unit mass of a yarn.”

Yarn Count Can Be Expressed In Two Ways :
- Direct System
- Indirect System
1. Yarn Count Measurement In Direct System:
In a direct yarn counting system, the yarn number or count is the weight of a unit length of a yarn.
Let,
N = The yarn number (Count)
W = The weight of the sample at the official regain in the units of the system.
L = The length of the sample
l = The unit of the length of the system.
Then,
N = (W × l)/L
Example: Tex, Militex, Kilotex, Denier, Jute( lbs/spyndle) etc.
2. Yarn Count Measurement In Indirect System:
In an indirect system, the yarn number or count is the number of “ units of length” per “ unit of weight”.
Let,
N = The yarn number (Count)
W = The weight of the sample at the official regain in the units of the system.
w = The unit of weight of the system
L = The length of the sample
l = The unit of length of the system
Then,
N = (L ×w)/(l × W)
Example: English count (Ne), Metric count (Nm), Worsted count ( Nw) etc.
Unit of Length & Weight in Direct Yarn Count System:

Count Calculation In Direct Yarn Count System:
Problem-1:
If a skim of 100 m of filament viscose yarn weights 1.67 gm. Calculate its Denier.
Calculation:
Here,
L = The length of the sample= 100 m
W = The weight of the sample at the official regain in the units of the system= 1.67 gm.
l = The unit of the length of the system
= 9 km
= (9 x 1000)m
= 9000 m
∴ N = (W × l)/L
= (1.67 gm ×9000 m)/(100 m)
= 150.3 den. (Ans)
Problem-2:
If a skim of 350 m of Polyester yarn weights 5 gm . Calculate its Tex.
Calculation:
Here,
L = The length of the sample= 350 m
W = The weight of the sample at the official regain in the units of the system= 5 gm.
l = The unit of the length of the system
= 1 km
= (1 x 1000)m
= 1000 m
∴N = (W × l)/L
=(5 ×1000)/(350)
= 14.28 Tex (Ans)
Unit of Length & Weight in indirect Yarn Count System:

Count Calculation In Indirect Yarn Count System:
Problem-1:
A lea of cotton yarn weights 25 grain. Calculate its count in the cotton or English system.
Calculation:
Here,
L = The length of the cotton sample
= 1 lea
= 120 yds (we know, 1 lea= 120 yds)
W = The weight of the cotton sample at the official regain in the units of the system
= 25 grain
= 25/7000 lb ( we know, 1 lb= 7000 grain)
=0.0036 lb
l = The unit of the length of the system
= 840 yds
w = Unit of weight of the system = 1 lb
∴ N = (L ×w)/(l × W)
= (120 ×1)/(840 ×0.0036)
= 120/3
= 40 Ne (Ans)
Yarn Count Conversion System:
- Conversion from Direct to Direct
- Conversion from Indirect to Indirect
- Conversion from Direct to Indirect
- Conversion from Indirect to Direct
For Unknown Count :
Unknown Count = Multiplying conversion factor × known count
Conversion Chart From Direct to Direct:

Count Calculation From Direct To Direct Yarn Count System:
For,
Denier to Tex,
Denier = 9 × Tex
For,
Tex to Jute,
Tex = 34.45 × Jute
For,
Tex to Denier,
Tex = 0.111 × Denier
Conversion Chart From Indirect to Indirect:
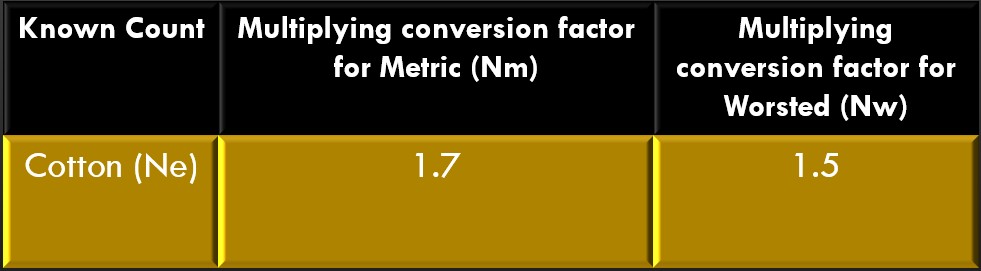
Count Calculation From Direct To Direct Yarn Count System:
For,
Metric to Cotton or English,
Nm = 1.7 × Ne
For,
Worsted to Cotton or English,
Nw = 1.5 x Ne
Conversion Chart From Direct to Indirect:

Count Calculation From Direct To Indirect and Indirect To Direct System:
For,
Denier to Cotton or English,
Denier = 5315/Ne
For,
Tex to Cotton or English,
Tex = 590.5/Ne
For,
Denier to Metric,
Denier = 9000/Nm
For,
Tex to Metric,
Tex = 1000/Nm
Mathematical Problem Related To Count Conversion:
Problem-1:
Find out the denier count, when Ne = 32 and Tex = 10.
Calculation:
We Know,
For,
Denier to Ne
Denier = 5315/Ne
= 5315/32
= 166.0 (Ans)
For,
Denier to Tex
Denier = 9 x Tex
= 9 x 10
= 90 (Ans)
Problem-2:
Find out the metric count, when Ne = 32 and Tex = 10.
Calculation:
We Know,
For,
Metric to Ne
Nm = 1.7 x Ne
= 1.7 x 32
= 54 (Ans)
For,
Metric to Tex
Nm = 1000/ Tex
= 1000/10
= 100 (Ans)
Relation Between Yarn Diameter & Count:
Let,
Yarn Count = N Tex [ For, Direct System]
∴ Length of N gm of yarn = 1 km
= 1000 m
= (1000 x 100) cm
= 105 cm
∴ Length of 1 gm of yarn = 105/ N cm
Assuming,
The specific volume of the yarn = 1.1 [ By experiment, an apparent specific volume of 1.1 for cotton was found]
∴ Volume of 1 gm of yarn = 1.1 cm3
∴ Length of the 1.1 cm3 of yarn = 105/N cm
We Know,
Volume = Length x Cross-sectional Area
or, 1.1 = 105/N x (πd2)/4 cm
or, d2 = (1.1 ×N ×4)/(105× π)
or, d = 0.375/100 × √N
or, d = k × √N
∴ d ∝ √N [For, Direct System]
For,
Indirect System,
1 inch = 2.54 cm
∴ d = = 0.375/100 × √N × (1/2.54) inch
In Indirect System,
We can assume Ne instead of Tex,
∴ Ne = 590.5/Tex
Or, Tex = 590.5/Ne
∴ d = 0.375/100 × √N × (1/2.54) inch
Or, d = (0.375 ×√590.5 )/(100 ×2.54) × (1/√Ne) inch
or, d = k x 1/(√Ne)
∴ d ∝ 1/√Ne [For Indirect System]
Methods Or Ways Of Yarn Count Measurement:
1. Warp Reel And Analytical Balance Method:
Overview:
This is a standard method used to determine the yarn count, which tells us how fine or coarse the yarn is.
Concept:
Yarn count is a numerical value that describes the thickness of yarn. There are two types of systems:
- Indirect system
- Direct system
Formula:
- Indirect system [N = (L ×w)/(l × W)]
- Direct system [N = (W × l)/L]
- N = The yarn number (Count)
- W = The weight of the sample at the official regain in the units of the system.
- w = The unit of weight of the system
- L = The length of the sample
- l = The unit of length of the system
Tools Required: Warp reel, weighing balance, and a set of standard weights.
Sample Used: Cotton yarn in hank form.
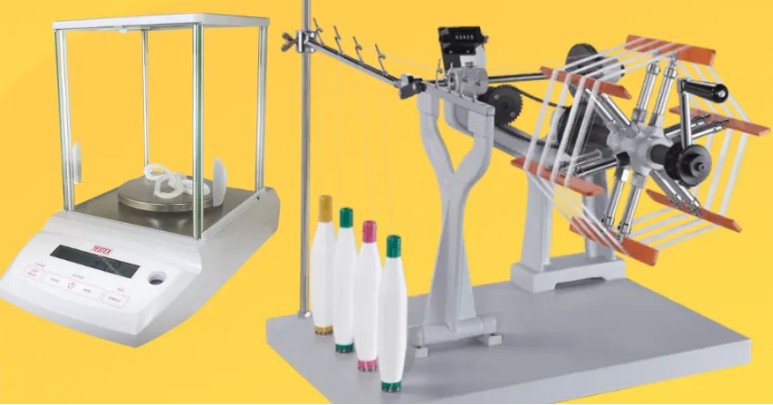

Working Process:
- The warp reel is set up and the yarn is guided from the cone through the reel.
- The reel’s counter measures the yarn length.
- For cotton, the reel has a 1-yard circumference and winds 120 yards. For jute, it’s 2.5 yards circumference with 300 yards needed.
- The cotton reel is motor-driven and stops automatically once the target length is wound; for jute, it’s operated manually.
- The wound yarn is then weighed using a balance.
- This process is repeated 12–16 times. The average is used to calculate the yarn count using the direct count system.
2. Warp Reel And Quadrant Balance Method:
Overview:
Quadrant balance is a direct-reading instrument used to determine the count of short yarn lengths.
Scope:
Can measure counts for yarns up to 40 yards. Also usable for weighing fabric samples.
Principle:
Measures the fineness or thickness of yarn using either:
- Indirect system [N = (L ×w)/(l × W)]
- Direct system [N = (W × l)/L]
Tools Required: Quadrant balance, scale, and blade.
Sample Used: Cotton yarn in roving or sliver form.
Working Steps:
- Measure 4 yards of cotton yarn with a scale.
- Hang the sample on the hook of the quadrant balance.
- Read the count directly from the appropriate scale.
- The balance includes three scales:
- 4 yards for sliver
- 20 yards for roving
- 840 yards for yarn
- Repeat the process 16 times and take the average to find the final count.
3. Warp Reel And Knowles Balance Method:
Structure:
- A beam balance used to find yarn count.
- It has a hexagonal rod with five faces (A to E), each calibrated for different count ranges.
- A screw allows rotation of the rod to bring the required scale into view.
- Matching weights (A to E) go with each scale.
- A sliding rider helps balance the beam.
Procedure:
- Place 120 yards of yarn on the right pan.
- Choose a matching weight (A to E) and place it on the left pan.
- Turn the screw to align the correct scale with the viewer.
- Adjust the rider on the scale until the beam is balanced.
- The rider’s position shows the yarn count.
4. Beesleys Balance Method:
Usage:
Used when only a short piece of cotton yarn is available, either loose or removed from fabric.
Principle:
- A beam with a hook on one end and a pointer on the other.
- The beam is leveled initially with a standard weight on the pointer side.
- Yarn samples are cut using a template and added to the hook until the pointer aligns with the reference line.
- The number of yarn pieces needed for balance gives the count.
Working Steps:
- Choose the right template based on yarn length (short or long cotton).
- Cut yarn pieces using the template and blade.
- Hang them one by one on the hook and count the pieces.
- Repeat the process 10 times and calculate the average for the final count.
Application:
Helps determine the count of yarn taken from a small fabric sample.
Some Important Conversion:
- 1 lb = 7000 grain
- 1 lea = 120 yds.
- 1 yds = 0.914 m
- 1 inch = 2.54 cm
- 1 kg = 2.204 lb
- 1 Hank = 840 yds.
References:
- Principles of Textile Testing by J E Booth.
- Handbook of Textile Testing and Quality Control by E. B. Grover, Elliot Brown Grover, Dame Scott Hamby.
- Physical Testing of Textiles by B.P. Saville.
To learn more on textile testing and laboratory accreditation you can check on the following article:
- Top 3 Effective method of Fiber length measurement
- Testing Of Textiles: Why Is It Important For The Textile And Apparel Industries?
- 10 comprehensive steps in textile fiber sampling method
- 5 EFFECTIVE insights of moisture regain in textile fiber
- Fabric Abrasion Resistance: Martindale Abrasion Testing Process
- Fabric Hand feel evaluation by Fabric Touch Tester (FTT)
- Color Fastness test
- Washing fastness test method: ISO 105 C06
- ISO/IEC 17025 Laboratory Accreditation Process
- ISO/IEC 17025 Laboratory Accreditation Advantages
- KEY STEPS FOR CONDUCTING AN EFFECTIVE QMS INTERNAL AUDIT




